MHC Class I
T cell receptors (TCRs) expressed on the surface of T cells specifically recognize and bind to complexes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and peptide fragments. CD8+ T cells, also called cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), recognize complexes of MHC class I molecules and peptide. CTLs directly kill target cells including virus-infected and cancer cells.
Preparation of MHC Class I Tetramer Reagents
MHC class I tetramer reagents are generated primarily using the method developed by Altman et al., who demonstrated that tetramers of MHC class I/peptide complexes could be used as probes for detection and quantitation of antigen-specific CTL (Science 1996, 274: 94-96)
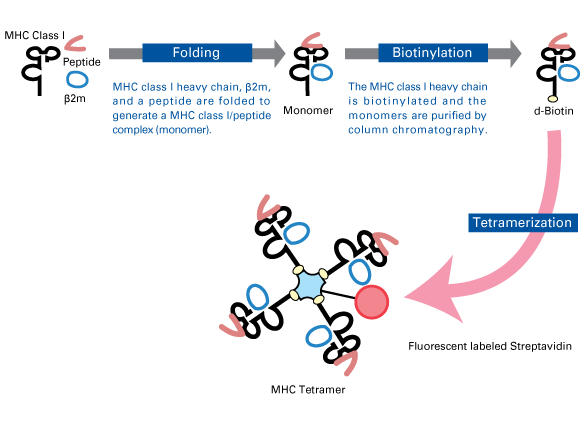
E. coli-expressed recombinant MHC class I heavy chain and β2-microglobulin (β2m) are folded in the presence of a peptide antigen to generate a soluble monomeric MHC class I/peptide complex (monomer). The monomer is then biotinylated by the biotin ligase enzyme, BirA, at a lysine residue present in the biotinylation sequence that has been added to the C-terminus of MHC class I heavy chain. The biotinylated monomer is purified by column chromatography. Purified biotinylated monomers are tetramerized by mixing with a fluorescently-labeled streptavidin to make MHC tetramer reagents.
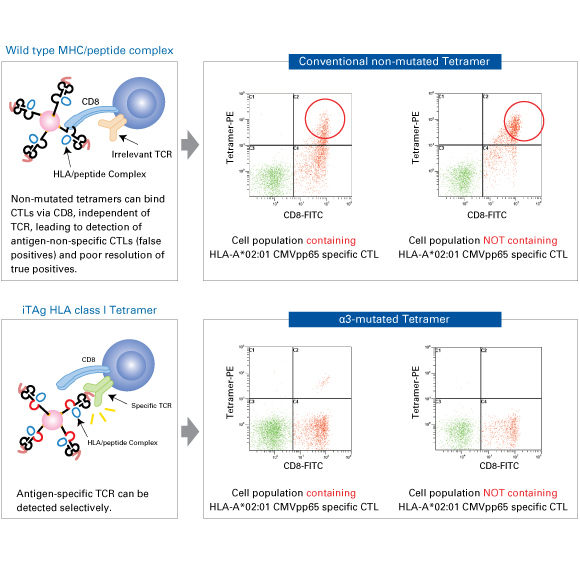
Greater specificity: The patented α3 mutation*
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the name of the major histocompatibility complex in humans. CD8 molecules are known to assist binding of HLA to CTL in vivo and thus HLA molecules have binding sites for CD8 molecules. Bodinier et al. reported that introducing a mutation (A245V) in the HLA class I heavy chain α3 domain minimized unwanted binding to CD8 molecules and dramatically improved specificity (Nat. Med. 2000, 6: 707). MBL has incorporated the patented mutation of the α3 domain in their HLA class I tetramers and is the only manufacturer of MHC multimers with this technology to enhance specificity for the antigen-specific T cell receptor.
*Only human and macaque HLA Class I Tetramers contain the alpha 3 mutation.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




