IL-33
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) family, such as IL-1α/β and IL-18, has important functions in host defense, immune regulation, and inflammation. IL-33, a member of the IL-1 family, that shows to induce T helper (Th) type 2 responses by signaling through the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 (IL-1R4), an orphan member of the IL-1 receptor family. Similarly to IL-1α/β and IL-18, IL-33 is synthesized as a 31 kDa precursor protein has been shown to be cleaved by caspase-1 in vitro. In vivo, IL-33 induces the expression of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and leads to severe pathological changes in mucosal organs. IL-33 has been originally identified as NF-HEV, which is a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in high endothelial venules. IL-33 may function as both a proinflammatory cytokine and an intracellular nuclear factor involved in transcriptional regulation.
IL-33 is also a member of the IL-1 family; however it differs from IL-1β in its activation control mechanism. Like IL-1α, IL-33 is present in the nucleus under normal conditions. Although the function of IL-33 as a nuclear factor remains elusive, its binding to the nucleosomal surface to suppress transcription has been demonstrated by in vitro experiments.
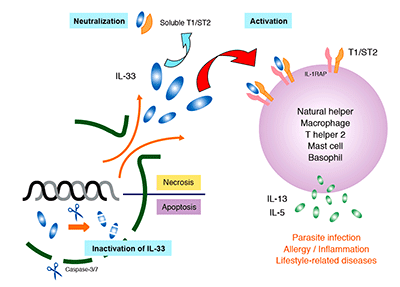 IL-33 is expressed in a variety of cells (including endothelial, epithelial, and fat cells) and tissues (such as the stomach, lungs, skin, lymph nodes, and kidneys). Since IL-33 is released during cell necrosis or tissue damage, is also suggested that IL-33 alerts the immune system after disruption to endothelial or epithelial cells has occurred. Its up-regulated expression is reported in the mouse brain and spinal cord. IL-33 is has been implicated in diseases ranging from parasitic infection and allergic diseases to arthritis, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, SLE, and Alzheimer’s disease.
IL-33 is expressed in a variety of cells (including endothelial, epithelial, and fat cells) and tissues (such as the stomach, lungs, skin, lymph nodes, and kidneys). Since IL-33 is released during cell necrosis or tissue damage, is also suggested that IL-33 alerts the immune system after disruption to endothelial or epithelial cells has occurred. Its up-regulated expression is reported in the mouse brain and spinal cord. IL-33 is has been implicated in diseases ranging from parasitic infection and allergic diseases to arthritis, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, SLE, and Alzheimer’s disease.