How to label antibodies
Method for labeling antibodies
How are the labels conjugated to antibodies in practice? Two types of labeling methods are commonly used depending on what part of the antibody is labeled. The first is to label the amino groups (NH2 groups) of the antibody (the NH2 type), and the second is to label the thiol groups (SH groups) (the SH type). Each method has advantages and disadvantages. The NH2 type and SH type methods are suitable for low and high molecular weight labels, respectively.
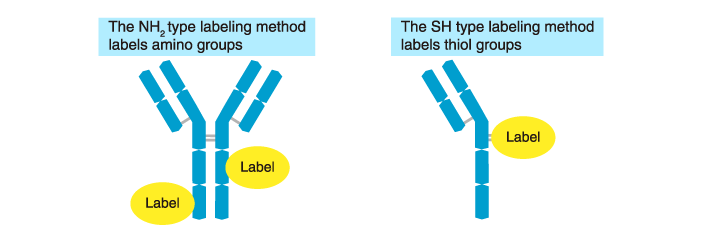
Labeling method: The NH2 type
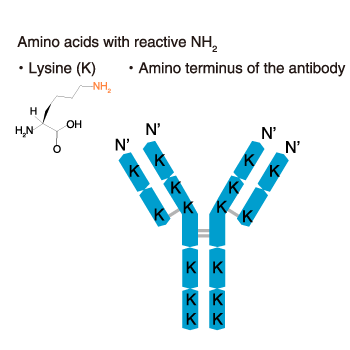
Labels are linked to the amino groups (NH2 groups) of antibodies.
Among the four amino acids with side-chain amino groups (glutamine, lysine, arginine, asparagine), only lysine can be labeled. In addition, the N-terminal amino group can be labeled. Thus, there are many sites that can be labeled as shown in the diagram below.
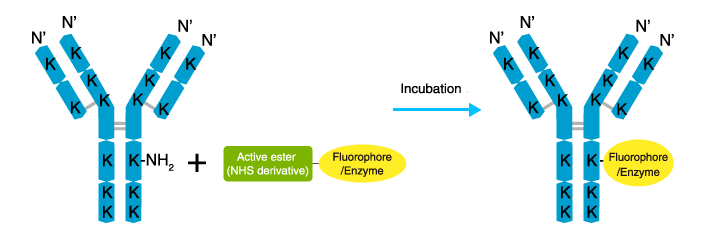
The procedure is relatively simple as shown. Antibodies are labeled by incubating with an active ester derivative of a fluorophore or enzyme. A number of active ester derivatives of fluorophores and enzymes are commercially available.
Advantages
- Simple procedure. Commercial kits are available.
- The addition of low molecular weight labels, such as FITC and biotin, to multiple sites enhances the sensitivity.
Disadvantages
- Excessive labeling can impair the activity of the antibody.
- High molecular weight labels, such as enzymes and PE, may cause steric hindrance and alter antibody activity.
Labeling method: The SH type (the maleimide method)
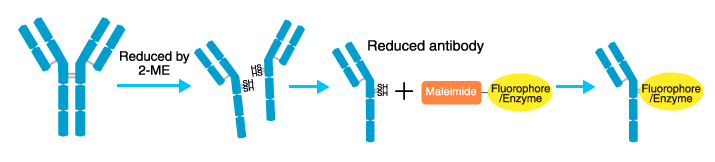
The SH type method that labels amino acids with an SH group (cysteine) is known as the maleimide method. The labeling sites are limited, and most are clustered at the hinge region. There are few cysteines in the variable region (antigen-binding site).
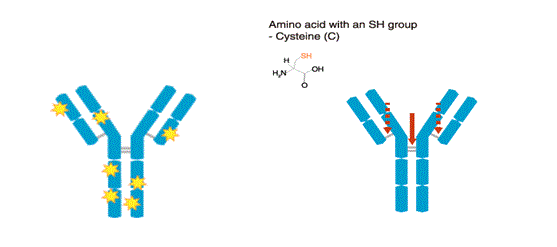
Antibodies are reduced by 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME), which splits the molecule at the hinge region. The SH groups of the reduced antibodies are reacted with a maleimide-activated fluorophore or enzyme.
Advantages
- High molecular weight labels, such as enzymes and PE, can be added without causing steric hindrance at the antigen-recognition site.
Disadvantages
- Multiple fluorophores and enzymes cannot be conjugated.
Detection methods
Direct method
Primary antibodies are pre-labeled with a fluorescent dye or an enzyme. Processing time can be reduced by the use of direct-labeled primary antibodies.
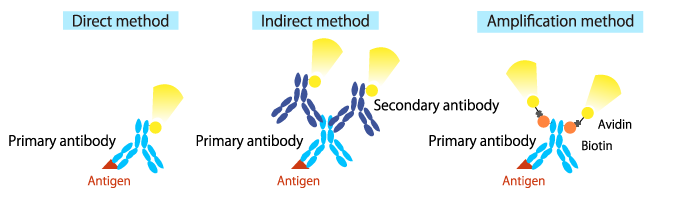
Indirect method
Primary antibodies are detected using a secondary antibody labeled with a fluorophore or an enzyme.
Amplification method
Primary antibodies are pre-labeled with biotin and detected by labeled avidin (the biotin-avidin complex).
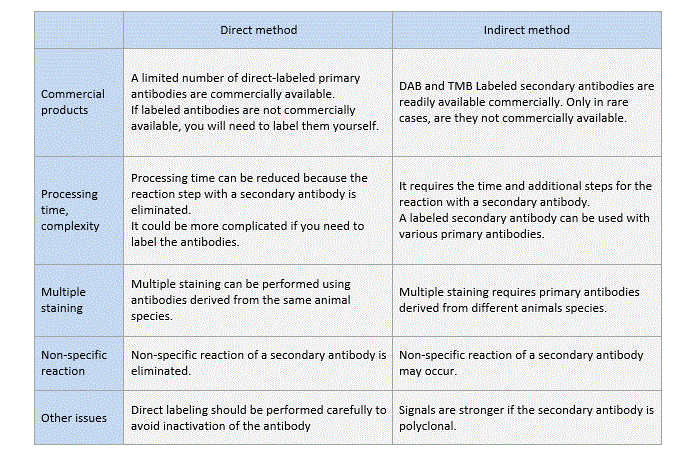
Comparison between the direct and indirect methods
Related Links
*Antibody
→Antibody basics
→Antibodies as a research tool
- How to select antibodies
- Labeled antibodies
- How to label antibodies
- Main causes of non-specific reactions
- How to reduce non-specific reactions
- Tags and Tag antibodies
*Qualitative and quantitative measurements of proteins using antibodies
- Western blotting (WB)
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)