The Principle and Method of Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The principle
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a method of target antigen (or antibody) capture in samples using a specific antibody (or antigen), and of target molecule detection/quantitation using an enzyme reaction with its substrate.
In ELISA, various antigen-antibody combinations are used, always including an enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody, and enzyme activity is measured colorimetrically. The enzyme activity is measured using a substrate that changes color when modified by the enzyme. Light absorption of the product formed after substrate addition is measured and converted to numeric values. Depending on the antigen-antibody combination, the assay is called a direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, competitive ELISA etc.

Direct ELISA
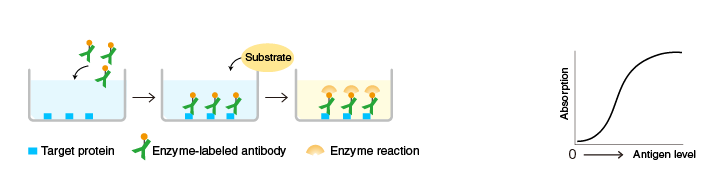
A target protein (or a target antibody) is immobilized on the surface of microplate wells and incubated with an enzyme-labeled antibody to the target protein (or a specific antigen to the target antibody). After washing, the activity of the microplate well-bound enzyme is measured.
Indirect ELISA
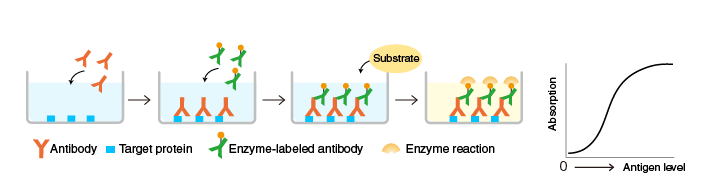
A target protein is immobilized on the surface of microplate wells and incubated with an antibody to the target protein (the primary antibody), followed by a secondary antibody against the primary antibody. After washing, the activity of the microplate well-bound enzyme is measured. Although indirect ELISA requires more steps than direct ELISA, labeled secondary antibodies are commercially available, eliminating the need to label the primary antibody.
Sandwich ELISA
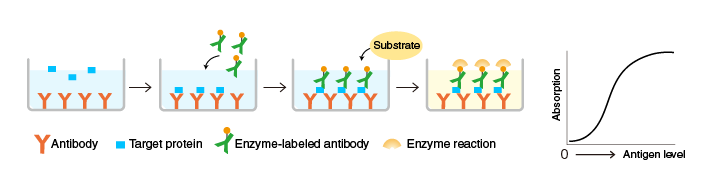
An antibody specific to a target protein is immobilized on the surface of microplate wells and incubated first with the target protein and then with another target protein-specific antibody, which is labeled with an enzyme. After washing, the activity of the microplate well-bound enzyme is measured. The immobilized antibody (orange) and the enzyme-labeled antibody (green) must recognize different epitopes of the target protein.
Compared to direct ELISA, the sandwich ELISA (combining antibodies to two different epitopes on the target protein) has a higher specificity. Sandwich ELISA is useful for applications that require a high accuracy.
Competitive ELISA
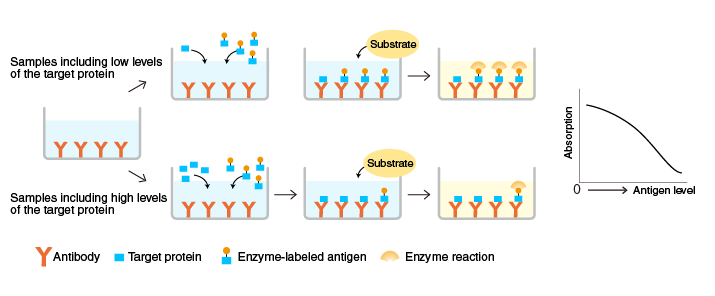
An antibody specific for a target protein is immobilized on the surface of microplate wells and incubated with samples containing the target protein and a known amount of enzyme-labeled target protein. After the reaction, the activity of the microplate well-bound enzyme is measured.
When the antigen level in the sample is high, the level of antibody-bound enzyme-labeled antigen is lower and the color is lighter. Conversely, when it is low, the level of antibody-bound enzyme-labeled antigen is higher and the color, darker. The graph above illustrates the correlation between absorption and antigen levels in samples.
When a target antigen is a small molecule, such as histamine, pesticide, and dioxin, two antibodies cannot simultaneously bind to the antigen in sandwich ELISA. Competitive ELISA is useful for the measurement of low molecular weight targets.
Immobilization of antibody/antigen on microplate wells
How are proteins bound (adsorbed) to the wells?
Immobilization is commonly mediated by hydrophobic interaction or covalent bonds. Microplates that are pre-activated for different immobilization methods are commercially available. The choice of method of immobilization depends on the type of protein to be immobilized. In general, covalent bonding is preferred for smaller molecules, such as peptides, and hydrophobic interaction (physical adsorption) is preferred for larger molecules, such as proteins. An appropriate method should be determined for each assay system.
Pre-treatment of microplates
Many types of ELISA microplates are commercially available, including the hydrophobic type, hydrophilic type as well as types surface-activated with amino or carboxyl groups. Surface-activated microplates are useful for covalent bonding. It is important to select the correct type of ELISA microplate for the intended use.
Procedure
Sandwich ELISA
An example performed at MBL







Related Links
*Antibody
→Antibody basics
→Antibodies as a research tool
- How to select antibodies
- Labeled antibodies
- How to label antibodies
- Main causes of non-specific reactions
- How to reduce non-specific reactions
- Tags and Tag antibodies
*Qualitative and quantitative measurements of proteins using antibodies
- Western blotting (WB)
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)